ISEMECO 3D D9 Understanding Facial Analysis: Techniques, Applications, and Future Prospects
ISEMECO 3D D9 Understanding Facial Analysis: Techniques, Applications, and Future Prospects
Facial analysis involves the systematic examination and interpretation of facial features in order to derive insights about an individual's physical and emotional state. The rise of technology has significantly enhanced the ways in which facial analysis is conducted, leading to numerous applications in areas such as healthcare, security, marketing, and personal wellness. This article explores what facial analysis is, the techniques used in the process, its applications, and its future prospects.
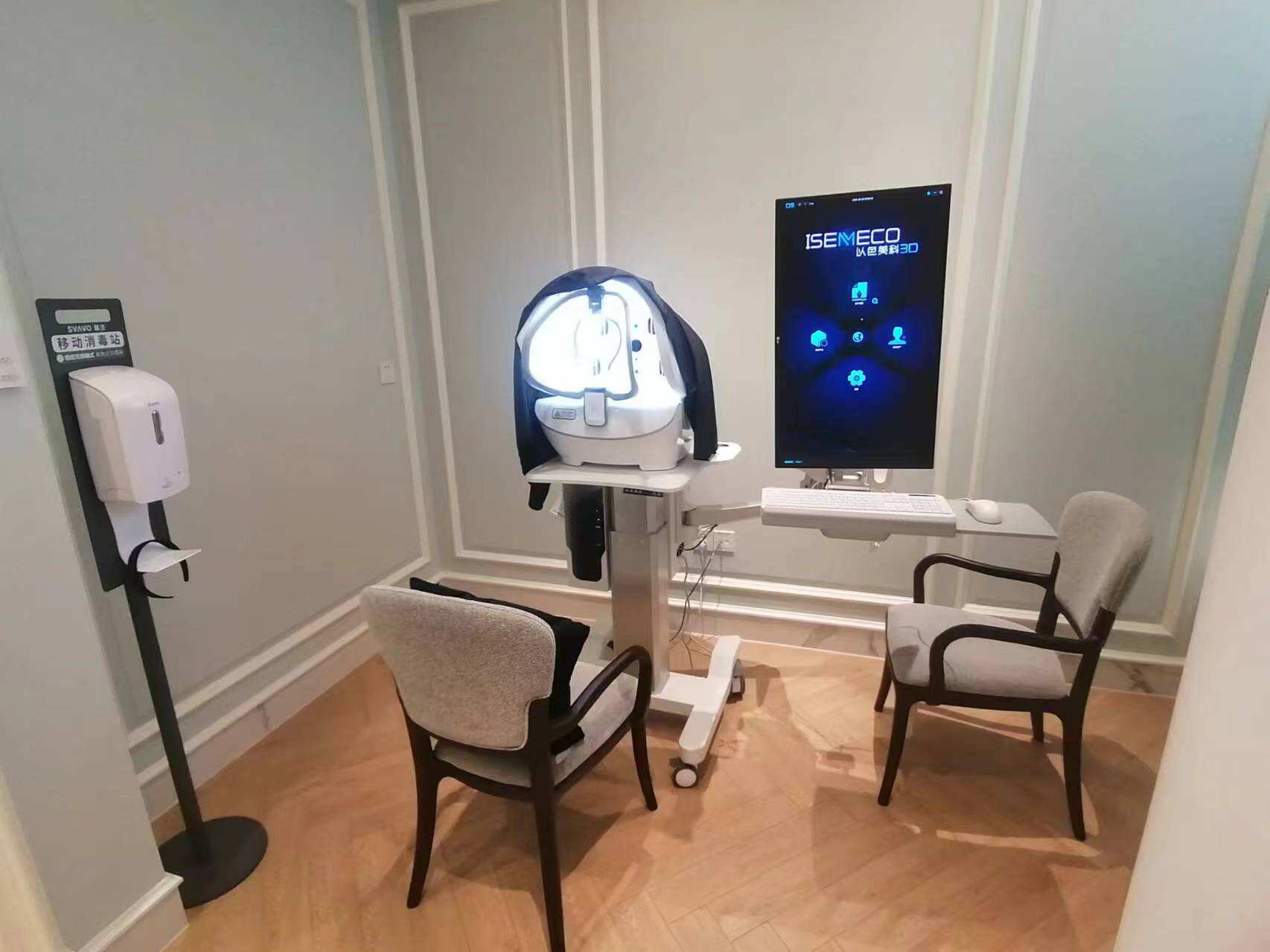
- What is Facial Analysis
Face analyze refers to the study of facial features, expressions, and characteristics to assess various aspects of human health and behavior. It combines the disciplines of psychology, dermatology, and computer vision to evaluate not only the physical attributes of the face but also the emotional states and psychological conditions of individuals.
- Techniques for Facial Analysis
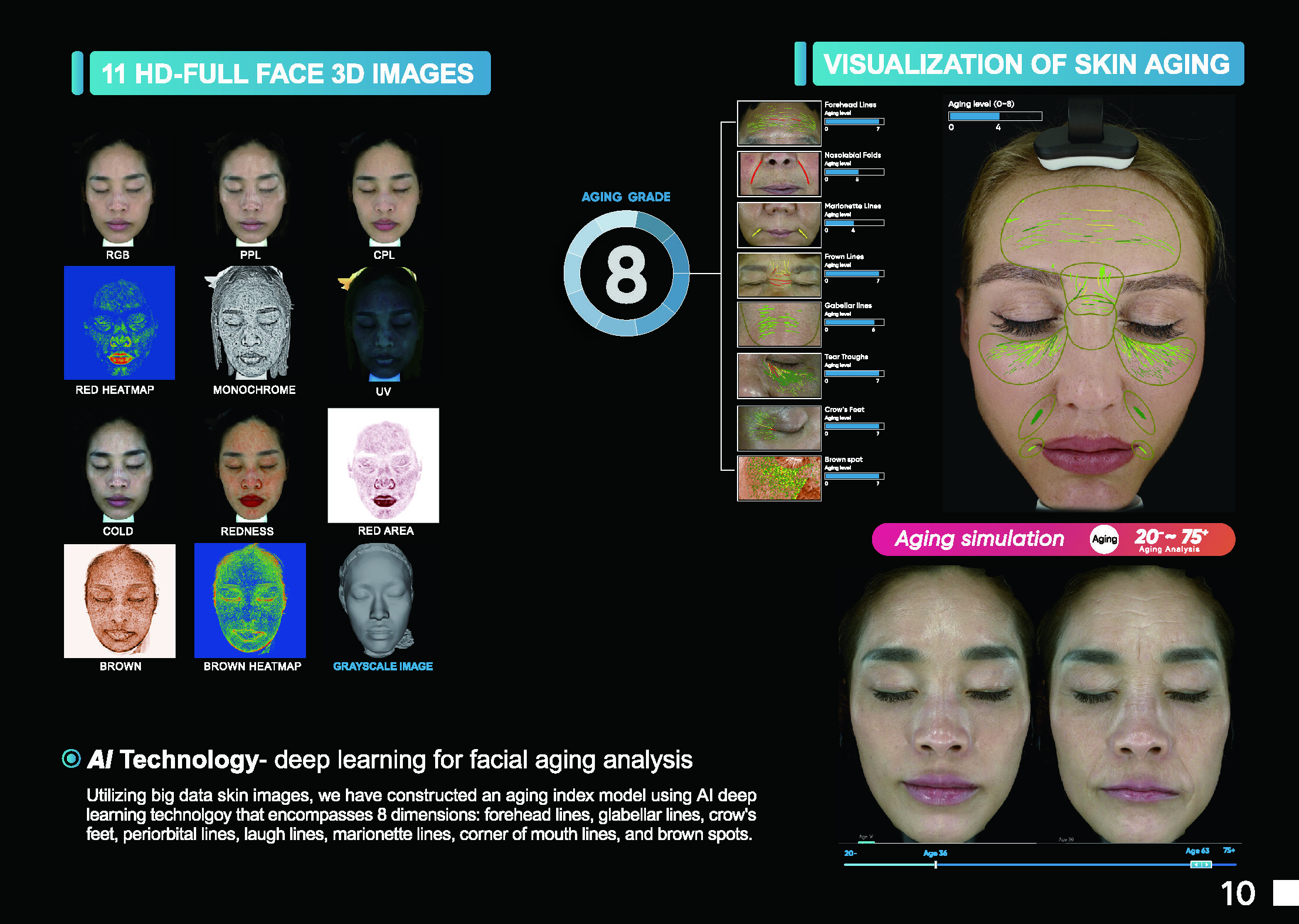
Traditionally, facial analysis was conducted through manual observation by trained professionals, such as psychologists or dermatologists. However, advancements in technology have paved the way for more sophisticated methods that utilize artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, allowing for quicker, more objective assessments.
various methods, which include:
1. **Visual Inspection**: This traditional method involves trained professionals analyzing facial features and skin conditions through direct observation. Factors such as facial symmetry, skin texture, color, and the presence of blemishes or wrinkles can be assessed.
2. **Photography and Imaging**: High-resolution images of the face are captured using cameras or specialized imaging devices. These images are then analyzed for clarity, symmetry, and anomalies.
3. **Colorimetry**: This technique assesses skin tone and pigmentation. Colorimetric analysis involves measuring the amounts of melanin, hemoglobin, and carotenoids present in the skin, providing valuable data about an individual's skin health.
4. **Digital Face Mapping**: Advanced facial analysis utilizes software to create a digital map of the face. Algorithms analyze various facial features—such as the eyes, nose, and mouth—to evaluate symmetry, proportions, and other characteristics.
5. **Facial Expression Analysis**: This method employs machine learning and AI to identify and evaluate facial expressions. Using optical recognition and deep learning algorithms, systems can detect emotions like happiness, sadness, anger, or surprise.
6. **3D Facial Scanning**: This cutting-edge approach involves scanning the face in three dimensions to create a detailed model. This model can be used to assess not only the surface features but also underlying bone structure, which can be useful for cosmetic procedures and medical assessments.
- How to Conduct : A Step-by-Step Guide
Conducting facial analysis can vary in complexity depending on the methods and tools used. Below is a simplified step-by-step guide that outlines a basic process for face analysis.
Step 1: Preparation
Before any analysis, it is essential to prepare the subject and environment. Ensure that the individual’s face is clean and free from makeup or other substances that may obscure features. Good lighting is crucial; natural light is often ideal, as it reveals true skin tone and texture.
Step 2: Image Capture
Capture high-quality images of the subject’s face from various angles. If using a facial analysis software, follow the guidelines to ensure proper positioning and distance from the camera. For more advanced techniques, 3D scanning devices may be used.
Step 3: Initial Assessment
Perform a manual inspection or use initial software tools to assess facial symmetry, skin condition, and overall facial structure. Note any areas of concern, such as acne, pigmentation issues, or visible signs of aging.
Step 4: Detailed Analysis
- **Digital Analysis**: If using specialized software, upload the captured images to the facial analysis program. The software will analyze features such as symmetry, texture, and emotional expressions.
- **Color Analysis**: Conduct colorimetric assessments to understand skin tone and identify potential underlying health issues.
Step 5: Interpretation of Results
Review the data generated from the analysis. Assess any identified issues, such as areas of increased pigmentation or specific emotional expressions. This is also the time to combine insights from visual inspection and digital analysis to provide a comprehensive overview of the subject’s facial health.
Step 6: Recommendations and Next Steps
Based on the findings, provide recommendations that may include cosmetic treatments, skincare routines, or further evaluations by health professionals if underlying conditions are suspected. If using the analysis for emotional or psychological assessment, appropriate referrals may be suggested.
- Applications of Facial Analysis
Facial analysis has a wide range of applications across various sectors including:
1. **Healthcare**: Dermatologists utilize facial analysis for identifying skin diseases, monitoring changes in skin conditions, and planning treatments.
2. **Cosmetics**: Cosmetic professionals use facial analysis to recommend skin care products tailored to individual needs, while brands analyze consumer preferences through facial expression techniques during product testing.
3. **Security and Surveillance**: Facial recognition technology powered by facial analysis is widely used for security purposes, including access control and identity verification.
4. **Marketing and Advertising**: Brands analyze consumer facial expressions in response to advertisements, allowing for targeted marketing strategies.
5. **Mental Health**: Expressions and emotions derived from facial analysis can be useful in therapeutic settings, aiding psychologists and counselors.
### Future Prospects
The future of facial analysis appears promising, especially with ongoing advancements in AI and machine learning. Technologies such as blockchain may enhance data security, particularly when analyzing sensitive information related to health or personal behaviors.
Moreover, as public perception of privacy evolves, the ethical use of facial analysis tools will necessitate transparency and user consent. With continued research and development, facial analysis could lead to breakthroughs in personalized healthcare and well-being, further enhancing its role in various fields.
- Conclusion
Facial analysis is an exciting and rapidly evolving field that blends technology with human health and behavior. Whether through traditional observation, advanced imaging techniques, or AI-powered assessments, facial analysis offers valuable insights into our emotional and physical well-being. As technological advancements continue to shape this field, we can expect to see increasingly refined methods and broader applications, ultimately benefiting healthcare, security, marketing, and personal wellness in unprecedented ways.
Editor: Henry
 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 SQ
SQ
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 UR
UR
 BN
BN
 LA
LA

